You might be exposed to ABS products daily without even realizing it: the housing of the fridge that you open every day is ABS, the dashboard of the car you take daily to work is ABS, and even the core material of the child’s Lego toy blocks is ABS.
This polymer,ABS acrylonitrile butadiene styrene has been quietly used in every aspect of life for decades. However, most individuals are only aware that it is ‘useful’ but do not know why it is so adaptable or how some of the different ABS products are manufactured.
To allow you to have a complete understanding of ABS, we’ve compiled the following guide, from its structure through to its applications, processing techniques, 3D printing techniques, and even practical examples in the medical field, to completely address the basic question of ‘what is ABS used for’.
Core Answer Summary
| Application | Specific Products | Key Reasons for Choosing ABS |
| Household Appliances Refrigerator | Air conditioner housings, washing machine panels | Impact-resistant, heat resistant, easy to color, low batch cost |
| Automotive Industry | Instrument panels, door Interiors, rearview mirrors | Low-temperature resistant, oil-resistant, light in weight for fuel savings |
| Consumer Electronics | Laptop housings, headphones, game controllers | Smooth surface, drop resistance, easy processing of fine textures |
| Toys/Medical/Industrial | Lego, surgical guides, toolboxes | High Toughness and Safety (Toys), Biocompatible and Sterilizable (Medical), Wear-Resistant and High-Strength (Industrial) |
Why Is JS So Reliable When It Comes To ABS Polymer?
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of ABS, you might ask: With all the ABS guides out there, why should I trust this one? The answer is simple—every assertion in this guide is backed by JS Precision Manufacturing’s over 10 years of direct experience in ABS acrylonitrile butadiene styrene processing.
JS has been focusing on custom ABS processing for years: We’ve made ABS housings in bulk for leading appliance manufacturers and custom impact-resistant ABS structural parts for automotive parts manufacturers. We’ve produced ABS 3D printing parts for startups and injection molding ABS parts with high accuracy for medical devices. In the process, we’ve summarized the key parameters and solutions to general problems of ABS injection molding, extrusion, and 3D printing.
This guide is a distillation of our practical experience, and only knowledge gained through actual testing can truly help you with ABS processing needs.
For ABS processing services, simply provide your product requirements and specifications. We’ll quickly provide a quotation and offer complete production support to achieve on-time delivery.
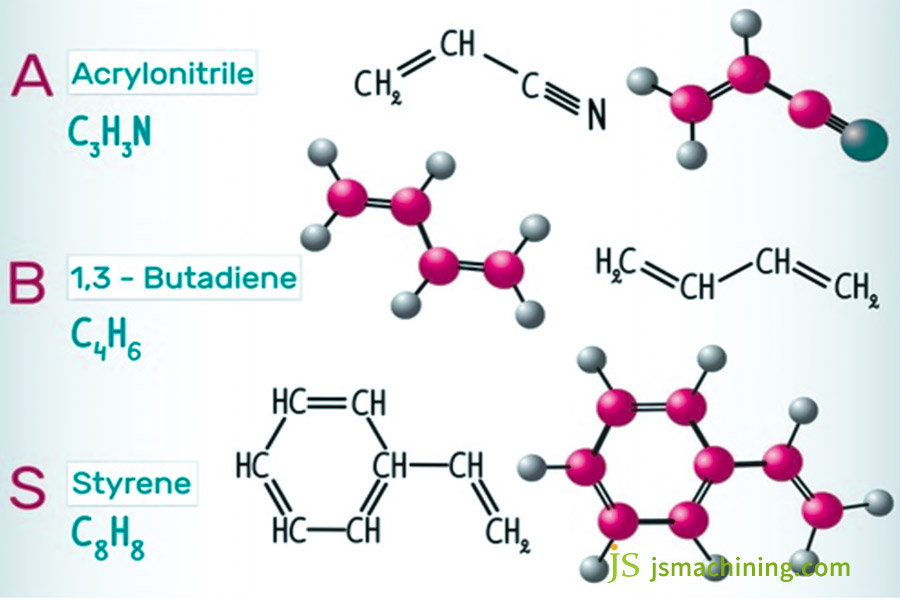
ABS: What Does It Stand For?
The majority of people know ABS is a plastic but are not quite certain that it is a solid combination of three components. ABS stands for acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, which means acrylonitrile (A), butadiene (B), and styrene (S). The three monomers are combined through the process of polymerization to produce the ABS polymer, which contains a variety of advantages.
Acrylonitrile provides chemical and heat resistance, a hard surface, and greater durability, butadiene imparts elasticity and low-temperature impact resistance to prevent brittle cracking, and styrene imparts good fluidity, ease of processing, and economy to ABS, enabling the manufacture of complex parts. These complementary properties are the fundamental reason why ABS acrylonitrile butadiene styrene has become a ‘versatile plastic’.
We possess in-depth knowledge of ABS material properties and can recommend suitable models based on your application scenario, providing custom 3D printing manufacturing. Simply inform us of your requirements, confirm your solution, and make your order. Our professional team will create high-quality ABS products for you.
The Ubiquitous ‘Hidden Champion’: A Panoramic View Of ABS Applications
ABS, with a balance of the advantages of performance, processability, and economics, is widely used in everything from general consumer goods to industrial and medical applications:
- Home Appliances: Exteriors of refrigerators/air conditioners, exteriors of washing machines, etc. Its impact resistance, heat resistance, and easy colorability are well-suited to mass production.
- Automotive: Instrument panel, door trim, rearview mirror housing, etc. Its low-temperature resistance and oil and lightweight construction reduce fuel consumption.
- Consumer Electronics: Laptop casing, headphones/game controllers, etc. Its low-friction, textured surface is drop-proof and can be finely textured.
- Toys and Leisure Products: LEGO bricks, helmet liners for children, etc. Its durability and toughness meet ROHS safety standards.
- Medical Devices: Instrument housing, surgical guides, etc. A medical-grade material that is sterilizable and biocompatible and can be 3D printing to meet special demands.
- Industrial Accessories: Toolbox housings, equipment protective covers, etc. Its chemical and abrasion resistance are high enough to support heavy loads.
Pellets To Finished Parts: The Art Of ABS Part Manufacture
ABS parts are manufactured primarily in three processes, namely injection molding, extrusion, and 3D printing, evolved to fit various requirements of manufacturing.
Injection Molding: The ‘Efficiency King’ of Mass Production
The most commonly used process of ABS is injection molding, best suited to mass manufacturing of complex parts (e.g., appliance casing and automobile interiors).
The basic concept is pouring molten ABS into a mold and removing it once cooled. The process is melting 220-260°C ABS pellets by heating them, injecting them high-speed into the mold, cooling with water to fix the shape, and demolding and cutting.
Its benefits are high efficiency (tens to hundreds of pieces per hour), high accuracy (precision ±0.1mm), and low cost of production. Disadvantages are in terms of very high mold cost, and therefore suitable for not low volume production runs or pilot runs.
Extrusion: A ‘Specialized Process’ for Long Products
If you need to produce long, sheet-type, or tube-type ABS products (ABS sheets, ABS tubing, ABS profiles), extrusion is your first preference.
It is the same procedure as injection molding, but ‘continuously extrusion’ in type: pellets are melted → continuously extruded into a mold → cooled → cut and reeled.
It possesses advantages of high speed (sheets can be produced at a few meters per minute speed) and variable lengths. It possesses disadvantages of being able to produce only products of simple cross-sections, but not complex structures.
3D Printing: A ‘Flexible Choice’ for Small Batch and Customization
Following advances in 3D printing technology, ABS has also emerged as a flexible 3D printing material, particularly for small batch production, prototyping, and customized components (e.g., personalized 3D printing parts for consumer electronics).
Printing of ABS acrylonitrile butadiene styrene is mostly dependent on FDM technology. The procedure is: 3D model slicing → Hotting of the nozzle (220-250°C) and hot bed (90-110°C) → Extrusion and deposition layer by layer → Cutting and post-processing.
Its benefits are no molds and very high flexibility, drawbacks are lower speed, less accuracy than injection molding, and higher cost.

Why Is ABS Applied Widely In Household Appliances’ Enclosures?
Home appliance housings require tough materials like impact resistance, heat resistance, colorability, and cost control. ABS has a lot to commend itself compared to the other materials. Relative comparison is as follows:
| Material | Impact Resistance | High Temperature Resistance | Colorability | Cost | Used for Home Appliance Components |
| ABS |
★★★★☆ (Wont be brittle at low temperature) |
80-100℃ |
★★★★☆ (Color retention good) |
★★★☆☆ (Controllable in a batch process) |
Housing, control panel |
| PP (Polypropylene) |
★★★☆☆ (Low temperature brittle) |
60-80℃ |
★★★☆☆ (Easily faded) |
★★★★☆ (Lower) |
Inner tub, base (not housing) |
| PC (Polycarbonate) |
★★★★★ (Very impact-resistant) |
120-130℃ |
★★★☆☆ (Easily faded) |
★★☆☆☆ (1.5-2 times more) |
Transparent window (not the whole housing) |
| HIPS |
★★★☆☆ (Lower than ABS) |
60-70℃ |
★★★★☆ (Texturing available) |
★★★☆☆ (Somewhat lower than ABS) |
Low-heat-generating housings (e.g., TV) |
PP and HIPS have shortcomings in performance, and PC costs are too high. Only ABS acrylonitrile butadiene styrene can balance all needs, making it a “standard” for home appliance casings.
We deal with specially designed ABS housings for domestic appliances, taking care of the process from material procurement to injection molding. You give us the size, color, and number of the housing, and we can create samples in no time for verification. On your approval, we can source large volumes and guarantee delivery efficiency and product quality.
Printing The ‘Future’: Secrets And Pitfalls Of 3D Printing ABS At Home
Secrets Core
Home 3D printing ABS is regulated by three variables:
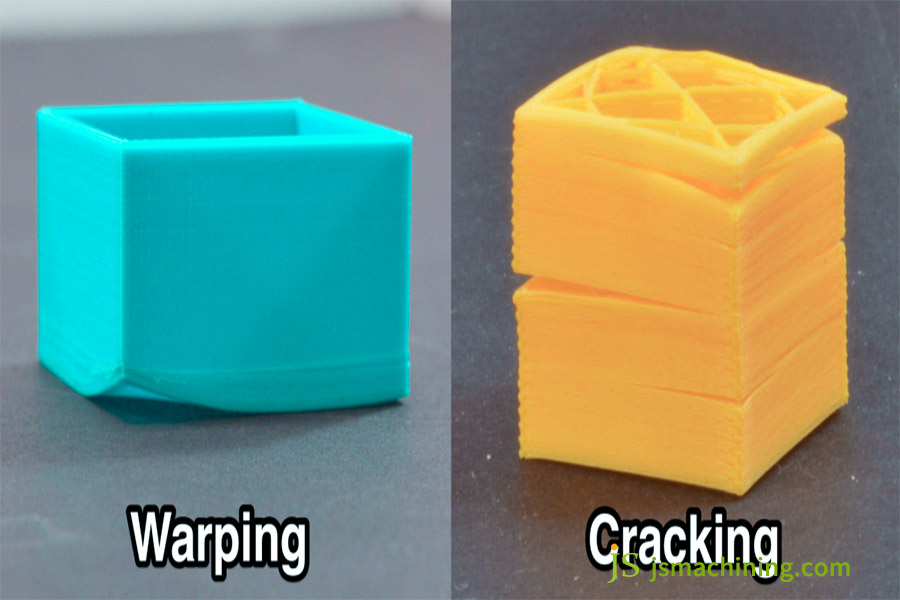
- Temperature: Nozzle 220-250°C (approximately 230°C), hot bed 90-110°C (approximately 100°C), print chamber 40-60°C (approximately 50°C) in order to prevent under-melting and warping.
- Humidity: Dry filament at 60-80°C (approximately 70°C) for 4-6 hours (approximately 5 hours) before printing. Store in airtight bag in order to exclude moisture, prevent bubbles, and cracking.
- Adhesion: Apply solid glue/ABS solution to hotbed. Reduce first layer speed by 50-70% (20-30 mm/s), and maintain thickness at 0.25 mm to prevent edge warping.
Common Pitfalls and Solutions
| Pitfalls | Symptoms | Solution |
| Part Warping | Edges warping or peeling off from bed | Increase bed/chamber temperature and print with a ‘support skirt’. |
| Layer Separation | Layers easily come off | Increase nozzle temperature, reduce speed, and print with dry filament. |
| Roughness | Cross-grain and low accuracy | Thin cuts (0.2 → 0.15mm), increase nozzle temperature, and sand. |
| Safety Risk | Strong odor | Ventilate print area and install an activated carbon air purifier to avoid prolonged exposure. |
Home printing is economical, but for high-precision parts, it is recommended to choose industrial grade services.Our online 3D printing services can meet such needs. Upload 3D models and deliver high-quality products in a short period of time.
Metallization: The Process And Difficulty Of ABS Electroplating
ABS electroplating covers chrome, nickel, or copper with light weight and processability but higher texture and wear resistance,making it the ‘best partner’ for plastic electroplating.
Difficulty Advantages
- Appropriate Ingredients: Butadiene roughening forms pits, thus the coating can be more easily stuck onto, while PP/PE surfaces are too smooth and hard to adhere to.
- Maturation Process: No special handling required, low cost suitable for mass production.
Core Process
This process is divided into five steps:
- Pretreatment :cleaning, roughening, neutralization, and removal of impurities to create ‘anchor points’.
- Activation:adsorption of precious metal particles to create catalytic centers.
- Chemical Plating:addition of a 0.5-2μm metal layer to create conductive base layer.
- Electroplating:external power source to add a 5-20μm metal layer to add thickness and improve performance.
- Post-treatment:cleaning, drying, and polishing to enhance appearance and longevity.
We have a seasoned ABS electroplating process and can adjust the coating type and thickness to your needs. Provide us with the ABS substrate and specifications, and we will design a plating plan. Upon approval, we will source and produce. We tightly manage each process to deliver a high-strength, high-quality coating.

Case Study: 48-Hour Printing: A Dream – The Miracle Of Medical ABS
Custom guides are required to position accurately in maxillofacial surgery, but the traditional process takes 1-2 weeks, making it a breeze to postpone the optimal treatment for patients. JS precision machining realizes the breakthrough employing medical ABS acrylonitrile butadiene styrene and 3D printing within 48-hour shipping.
Customer Challenge
The maxillofacial surgery instrument firm they worked with had to endure four major challenges:
- Extremely high precision requirements, guide misregistration by more than 0.1mm would cause complications.
- The material had to meet ISO 10993 standards, be tough, and sterilizable.
- Within 72 hours from obtaining CT data to delivering sterilization guide plates.
- Metal and PLA-printed guides were not able to meet these requirements.
JS Solution
- Material Selection: ISO 10993-1 compatible medical-grade ABS was selected, which possesses biocompatibility, excellent mechanical properties, and sterilization compatibility.
- Data Analysis and Design: CT data was reconstructed to a 3D model employing the Mimics software. Guide plate tolerance was ±0.05mm and for the guide hole, it was ±0.02mm, as confirmed through web search.
- Precision Printing: Using an industrial grade SLA printer with a layer thickness of 0.025mm and an accuracy of ± 0.05mm, printing can be completed in 4 hours, which is half faster than FDM. It can also ensure a smooth guide surface and prevent bacterial growth – this is a typical high-precision application of custom 3D printing in the medical field.
- Post-Processing and Certification: Clean and solidify, finely polish, sterilize with ethylene oxide for 4 hours, and provide a complete quality report.
Final Outcome
The guide plate had a tolerance of only 0.03mm, was delivered within 42 hours, and weighed 15g (60% reduced). The patient experienced no significant intraoperative discomfort, surgery time was shortened to 2 hours, and the recovery was accelerated. Over 10 following sets were delivered within 48 hours, helping the client increase diagnostic and treatment efficiency.JS was awarded the qualification of ‘Priority Partner’.
FAQs
Q1: Is ABS plastic toxic?
Untreated, pure ABS resin by itself is not toxic and is widely used in food packaging and toys. However, when heated during processing, it can release trace amounts of irritating vapors (primarily because of butadiene)Therefore, it is recommended to perform 3D printing ABS and other processing operations in a well ventilated environment to avoid gas accumulation.
Q2: Are ABS parts bondable with glue? If so, what kind of glue?
Yes, and it’s easy! Acetone or plastic glue specifically designed for ABS has the best bonding effect.They dissolve slightly into the plastic surface, and after the solvent evaporates and dries,The two parts can be tightly fused together at the molecular level to form a very strong connection.
Q3: What are the benefits and limitations of ABS compared to ASA (acrylonitrile-styrene-acrylate)?
ABS has good impact resistance and is economical too, and thus can be employed in most applications, including home appliances and vehicles. It does not have good weather resistance and will age and become discolored because of prolonged exposure to the weather. ASA possesses excellent weather and UV resistance, and therefore ought to be employed for exterior uses. While, it is less impact-resistant than ABS but only slightly, and it costs more, therefore the choice would be on an application basis.
Q4: Why is my clear ABS print not transparent?
The so-called “transparent” ABS materials on the market are mostly in a semi transparent state rather than completely transparent.Opacity after printing is largely caused by light scattering due to internal layer grains, tiny bubbles, and surface roughness. Post-processing (e.g., acetone vapor polishing) can be used to improve high transparency through dissolving surface grains and reducing scattering.
Summary
ABS acrylonitrile butadiene styrene is no ‘specialist’ in a single field, it is an all-rounder in a range of industries, ranging from home appliances, automotive, and consumer electronics to medical and toys. It is appropriate for application in everyday household items like refrigerator housings and in highly accurate medical applications like surgical guides, it can be manufactured in high volumes by injection molding or customized by 3D printing.
JS Precision Manufacturing’s deep understanding of ABS is the result of extensive practical experience in ABS processing. We can provide individual ABS solutions for customers across a range of industries based on user demands.If you have specific ABS processing needs, JS Precision Manufacturing is always ready to provide you with professional support and transparent 3D printing prices, enabling this ‘hidden champion’ material to truly serve your product or project.
Disclaimer
The content of this website is for reference only. JS series expressly disclaims any representations or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information provided. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, design features, material specifications or processes mentioned should not be considered as any commitment or guarantee by JS for products offered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers on its network or other channels. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for confirming their specific needs and product suitability. If you have any questions or need further information, please contact JS directly.
JS Team
JS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. We have over 20 years of experience with over 5,000 customers, and we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal manufacturing,3D printing,Injection molding,Metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with over 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers, ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it is small volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseJS TechnologyThis means selection efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, visit our website:jsmachining.com


Pingback: Is FDM Printing Better Than MJF? - JUSHENG
Pingback: What Is The Quotation Structure Of SLS 3D Printing? - JUSHENG