When mass-producing customized gifts, like needing milling 3D models on wood boxes and engraving intricate patterns on acrylic cover panels, you would be torn between a CNC and a laser engraver. Both are widely used machines for machining but for very different applications. Wrong choice leads to cost-intensive and time-wasting projects.
This guide will help you identify precisely which machine best fits your needs, considering its operating concepts, key differences, cost, and practical examples. It will also leverage JS’s hands-on experience to allow you to successfully align your needs and choose the most appropriate technology for your project. This guide will also cover laser cutting applications.
Short Overview Of Key Answers
| Comparison Dimension | CNC Engraver | Laser Engraver | Key Difference |
| Core Capability | 3D three-dimensional milling with strong metal shaping capability. | 2D fine engraving/cutting with high efficiency. | CNC focuses on “shaping”, while laser focuses on “precision”. |
| Applicable Materials | Hard materials such as metal and wood. | Non-metals (e.g., acrylic) plus fiber laser for metal cutting. | Material compatibility is complementary. |
| Precision Level | Up to 0.01mm (structural precision). | Up to 0.001mm (detail precision). | Laser has better detail processing performance. |
| Initial Cost (Basic Model) | 5,000 – 20,000 US dollars. | 3,000 – 15,000 US dollars (CO₂ type). | CNC requires higher initial investment. |
Why Are They Complementary? JS’s Hands-On Experience Sharing
Prior to discussing CNC and laser engravers’ complementary relationship, let us first take a glimpse of JS’s actual experience. With over 10 years of machining history, we’ve performed over 5,000 custom work orders for various industries like automotive, consumer electronics, and medical devices.
For example, in the production of aluminum engine brackets for motor vehicle parts manufacturers, we employ CNC milling to achieve complex 3D shapes, concurrently using laser cutting to engrave logos on bracket surface. In producing acrylic control panels for smart home manufacturers, accurate hole positioning is achieved using laser cutting, as CNC forms the panel’s edge radius.
These experiences have given us a deep understanding of the advantage of both types of equipment. This book, a condensation of our experience over many years, can help you avoid selection errors.
JS has extensive experience with CNC and laser machining and offers laser cutting services. If you have a requirement, we invite you to contact us in order to discuss your proposal. After confirmation, we can order immediately to allow you to finish your project in an efficient manner.
Working Principles Revealed: Rotating Tool Vs. Focused Photons
Now that we have some knowledge about our experience, let’s learn about how CNC and laser engravers function. Understanding how they function will make you understand better why they are suited for different situations.
How Do We Use a CNC Engraver?
Essence: “Subtractive Manufacturing.”
Process:
The operator first loads the designed 3D model into a CNC system. The system converts the model data into machine motion commands. The spinning tool of the CNC engraver machine (traditionally operating between 8,000-20,000 rpm) subsequently performs these commands, removing away excess material gradually from the work surface of the workpiece, ultimately producing the required 3D shape.
For example, when machining metal parts, the tool mills through a pre-programmed path, providing real-time dimensions feedback to ensure that all the dimensions are as specified.
How does a laser engraver work?
Essence: “Heat processing” or “ablation.”
Process:
A high-power laser beam is generated by a laser generator that is then concentrated by a focusing lens into an extremely tiny spot with a diameter of 0.1-0.5mm and aimed at the workpiece surface. The workpiece surface material rapidly heats up and melts, vaporizes, or ablates when it absorbs laser energy.
At the same time, the laser beam moves along a predetermined path at 50-200 mm/s, giving an inscribed pattern or eliminating the shape on the workpiece. For example, in laser cutting, the laser beam is able to etch cut through plastics like acrylic and metals.
JS Precision Manufacturing has experience working with both CNC milling and laser cutting. We can select the proper equipment based on your requirements for a workpiece to deliver quality. We can detail the processing process at any moment you reach out to us.

In-Depth Analysis: Six Core Differences Determine Your Choice
Now that we have a grasp of how both work, let’s dive deeper into the six fundamental differences between them. These differences will have a direct impact on which machine to use. The table below lays it out visually:
| Comparison Dimension | CNC Engraver | Laser Engraver |
| Processing Method & Physical Contact | There is physical contact, and it relies on cutting tools to cut workpieces. | There is no physical contact, and it relies on laser thermal action to process workpieces. |
| Material Compatibility | Suitable for various hard materials such as metal, wood, and plastic. | Suitable for non-metals (e.g., acrylic, fabric), and fiber laser is needed for metal processing. |
| Cutting & Engraving Capability | Good at 3D three-dimensional engraving and cutting, and can handle complex curved surfaces. | Good at 2D flat fine engraving and cutting, with high efficiency. |
| Precision & Details | Precision can reach 0.01mm, which is suitable for structural precision requirements. | Precision can reach 0.001mm, which is suitable for detailed pattern engraving. |
| Post-processing & Operational Complexity | Burrs may appear after processing and need grinding, and professional training is required for operation. | The edge is smooth after processing, the operation is relatively simple, and familiarity with software is required. |
| Safety & Environmental Considerations | Tool wear occurs, and metal chips are generated which need to be handled. | Smoke may be generated and requires a smoke exhaust system, and some lasers have radiation risks. |
As the table amply indicates, both have strengths in most aspects. You’ll have to decide depending on your particular processing requirements.
- To create 3D curved shapes on solid wood furniture legs, a CNC engraving machine offers smooth curves.
- To create complex shapes on clothing fabric, a laser engraver can achieve the desired effect in a flash without ripping or destroying the fabric fibers.
- When metal nameplates are being cut, if you need three-dimensional chamfers at the edges, a CNC is better suited. If only surface engraving is required, a laser engraver is better suited.
- If you need precise non-metal parts, a laser engraver is preferable.
Cost Comparison: Which Is More Cost-Effective?
Aside from the inherent differences, cost is also a consideration for everyone. Let’s take a look at the cost-effectiveness of CNC versus laser engraving, complete with laser cutting prices.
Initial Equipment Cost
CNC engraving machine: Initial costs are generally high, with a bare minimum three-axis CNC machine costing anywhere from $5,000 to $20,000. 5 axis CNC machines for complex curved surfaces can be much more expensive.
Laser engraver: Costs are relatively low at the outset, with a basic CO₂ laser engraver costing between $3,000 and $15,000. Fiber laser engravers, due to their higher technical requirements, cost between $8,000 and $30,000.
Operating Costs
CNC engraving machine: The expenses are largely sourced from two areas: tool wear (metalworking tools cost between $50 and $200 each and require constant renewal) and guideway maintenance (every year, the cost of repairs runs between $200-500, with regular lubrication required).
Laser engraver: The primary source of energy comes from laser tubes (CO₂ laser tubes cost $200-$500 per unit), and the energy consumed is usually only 50%-70% of the energy consumed by CNC engravers, cutting down on electricity bills in the long run.
The Impact of Processing Quantity on Cost
Processing 1,000 acrylic signs: Laser engravers offer faster processing speeds (around 50 per hour), with total costs being approximately 30% lower than those of CNC engravers.
Machining 500 stainless steel parts: CNC engravers can do multiple processes in a single pass with unit costs 15% lower than that of the fiber laser engraver.
For long-term large-scale processing of metal parts, CNC has lower unit costs. For short-term precision machining of non-metallic parts, laser has a cost advantage.
JS can provide you with affordable online laser cutting services. We’ll obtain laser cutting prices from your processing amount to provide you with value for money. Interested ones can obtain a quote and place an order upon confirmation.

Metal Processing Capabilities: Who is the King?
Metal processing customers want to know whose capabilities for metalwork are superior: a laser engraver or a CNC. We’ll answer the question below, along with information regarding metal laser cutting.
Metal and CNC engravers
It’s the first choice for processing metals because CNC engravers use rotating cutters to directly perform milling, drilling, and cutting on metal, changing the overall shape of metal workpieces.
Processing parameters are adjusted based on the level of hardness of the metal. For example, aluminum alloys are given cutting speeds of 100-300 m/min, while the stainless steel is given 50-150 m/min reduced speeds in order to ensure effectiveness and precision.
For example, machining solid aluminum billets into complex mechanical parts ensures the structural integrity and dimensional accuracy of metal workpieces, making them suitable for 3D metal structure processing needs.
Metal and laser engravers
There are two types of laser engravers: CO₂ lasers and fiber lasers.
CO₂ lasers have a longer wavelength and poor absorption capacity with metals, which typically only mark or slightly engrave on metal surfaces. Fiber lasers, on the other hand, have a short wavelength (power 500-2000W) and can be efficiently absorbed by metals, enabling metal cutting and deep carving.
For example, when performing metal laser cutting, a 1000W fiber laser can cut 8mm stainless steel and a 2000W can cut 15mm aluminum alloy with high precision.
Unusual Key Points
Laser metal processing is more of a “surface treatment,” such as engraving logotypes or marking dimensions on metal surfaces. CNC metal processing, on the other hand, is more of a “shape modification,” such as machining a metal block into a component with grooves or thread holes. The efficacy and depth of the two methods are markedly different.
JS has expertise in metal processing and offers professional metal laser cutting and CNC metal processing. In case of requirement of metal processing, kindly contact us and we will develop a suitable solution for you.
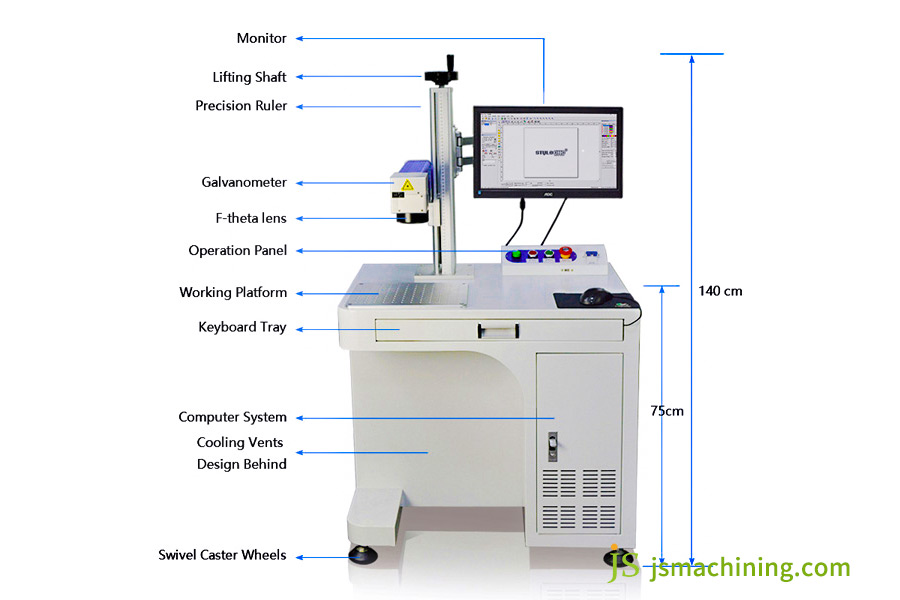
Practical Example: Joint Creation Of Laser Cutting And CNC Milling
Next, based on a practical example, we will explain how laser cutting and CNC milling can be combined to meet complex processing requirements. The example will also deal with applications in relation to custom laser cutting manufacturing.
Customer Needs
- Product Type: High-end customized mechanical keyboard, intended batch production of 500 units.
- Aluminum Base Specifications: Ergonomically milled, reserved countersink screw holes (so screw heads won’t protrude when assembled), and exactly aligned to the holes in the acrylic plate.
- Acrylic Switch Plate Specifications: 3mm thick, with a neatly cut switch hole pattern and laser etched brand logo to offer a stylish appearance.
JS’s Solution
CNC machining operations: A three-axis CNC milling center (spindle speed 12,000 rpm) was utilized to machine the keyboard base from a solid aluminium billet of thickness 5mm. The operations involved:
- Machining the overall flat surface to get the flatness of the base.
- Machining an ergonomic tilt angle to ensure greater user comfort.
- Machining reinforcing ribs to ensure greater structural strength.
- Machining countersunk screw holes and drilling, maintaining dimensions while machining with an error of less than 0.01mm.
Laser cutting machine operation: A 100W CO₂ laser cutter was used to cut a 3mm thickness acrylic sheet. Work involved:
- Cutting out the switch hole pattern corresponding to the CNC base with a spacing error of less than 0.001mm.
- Engraving the company logo of the customer with a low power setting at 30%.
- Acrylic with smooth, burr-free edges, without the need for follow-up polishing.
Results
After processing for a week, there were 500 units of aluminum bases and acrylic positioning plates that were completed. Customer feedback after assembly: fit was excellent, switches were installed snugly, and the keyboard was a pleasure to type on. The transparent and beautiful logo on the acrylic plate served to give the product an upper-class touch.
This project, in combining the merits of CNC and laser technology, had attained a perfect balance between form and function, demonstrating the potential of hybrid manufacturing and winning much customer praise.
CNC and laser collaborative manufacturing is very well expertized by JS Precision Manufacturing, which offers custom laser cutting manufacturing services. If you have the same complex machining requirements, please feel free to contact us for consultation.
CNC Or Laser Engraver: Which To Choose?
Now that you’ve read this case study, you may still be wondering: Should you use CNC or laser engraver? The answer is simple: it is based on your specific requirements, for instance, whether you require online laser cutting services and whether or not the machining cycle is immediate.
If one needs to machine metal components of 3D shape, such as mechanical brackets or metal enclosures, and need overall shape transformation of the workpiece, then a CNC engraver would be more suitable since it can perform detailed 3D milling with structural strength and dimensional accuracy preserved.
If you are machining hard and brittle materials (glass or ceramics), then a laser engraver would be more suitable because it is contact-less and less likely to chip or break. Brittle material CNC machining can have greater scrap rates.
If you need to machine 2D non-metal workpieces, such as acrylic boards or cutting clothes, or engrave accurate patterns or logos on the workpiece surface, then a laser engraver would be better suited because it offers superior 2D machining efficiency and finer precision.
If your order is urgently pending and cannot be postponed, then a laser engraver is suitable for 2D workpieces because it has quicker setup times (about 1-2 hours). A CNC engraver requires parameter settings and tool changes, and this will require approximately 3-5 hours.
In case you want a 3D metal frame and accurate 2D finish, for example, the mechanical keyboard in the above example, you can have both used simultaneously. JS can offer hybrid processing solutions and online laser cutting services.

Breaking Through Tradition: Hybrid Technology And Future Outlook
With the development of processing technology, classical CNC and laser engraving are continually evolving, and hybrid technology is turning into a new trend. Let’s discuss future development, such as information pertaining to laser cutting parts.
Key Characteristics of Mainstream New Processing Technologies
Hybrid Machine Tools (CNC + Laser)
- Basic Configuration: With a dual-spindle facility (tool milling axis + laser processing axis).
- Core Advantages: Allows CNC’s 3D processing power to be combined with laser’s precision laser cutting and engraving power so that a single device can perform multiple processes.
- Increased Efficiency: Reduces workpiece handling time by over 50%, preventing accuracy losses caused by secondary clamping. For example, milling a metal 3D figure in the first place and then laser engraving the mark directly.
Waterjet Cutting Technology
- Working Principle: Utilized a 300-600MPa high-pressure abrasive water jet with an abrasive (e.g., garnet) to cut the material.
- Applications: Machines heat-sensitive materials (e.g., titanium alloys, glass, ceramics) with no thermal deformation.
- Limitations: Less precision than laser (typically 0.05-0.1mm), suited for roughing. High precision laser cutting parts still require laser cutting.
Future Intelligent Development Directions
- Laser engravers will incorporate AI autofocus capabilities integrated within them that allow real-time recognition of variations in workpiece surface heights and focal distances, further raising the precision of machining.
- CNC machines will utilize digital twin technology to virtually model the machining process in advance, pre-resolving issues like collisions and dimensional errors, and reducing scrap rates.
- Laser cutting machines shall be equipped with a real-time quality inspection system on the basis of a camera to take photographs of cutting edges and dynamically change parameters for uniform quality of laser cutting parts.
JS is also keeping a close eye on developments in these technologies and will bring in newer machines to provide customers with more efficient service and quality laser cutting parts and CNC machining parts.
FAQs
Q1: How is engraving depth achieved?
How engraving depth is achieved varies immensely depending on equipment type. Engraving equipment using the CNC technique will control the cutting depth of the tool by setting the tool’s cutting depth. Before processing, the operator programs parameters so that the workpiece is penetrated by the tool at a predetermined vertical distance, thereby reaching a predetermined depth. Laser engraving machinery relies on laser power as well as passes. Higher power offers deeper engraving per pass.
Q2: Can CNC and laser engraving be performed simultaneously on the same machine?
Yes. There exist hybrid machines incorporating both CNC and laser technology. They consist of a tool milling module and a laser processing module with an integrated control system. In this way, CNC 3D engraving and laser fine-detail engraving can simultaneously be performed on the same machine without the changeover of the workpiece during processing, thereby saving handling time, avoiding precision errors caused by secondary clamping, and substantially improving processing efficiency.
Q3: What are the differences between the two technologies in terms of waste produced, and what is it used for?
The waste produced and how it should be handled differ considerably between the two technologies. Solid waste and powder such as metal shavings and wood chips are produced by CNC engraving machines, which can be handled by recycling them using the machine’s dust collection system. Fumes and gases containing poisonous substances emitted by laser engraving machines must be cleaned and evacuated through a professional exhaust system to avoid environmental and health impacts.
Q4: Why can’t lasers cut or engrave through transparent materials?
The principal reason is that transparent materials are excessively transmissive to lasers and cannot absorb laser energy efficiently. For example, the most commonly used CO₂ laser has a wavelength of 10.6μm. Though it can be absorbed by the majority of non-metallic materials, regular glass and transparent acrylic are highly transparent to this wavelength. The majority of energy travels through the material and fails to provide sufficient heat accumulation for processing.
Summary
Which is superior, CNC or laser engraving? There is no correct or incorrect answer. They are the “right and left hands” of the machining world, each with a special set of traits. CNC is a “body transformation master,” performing 3D metal processing with optimal results, laser is a “fine beautician,” performing 2D non-metal engraving and metal laser cutting.
Your needs dictate your preference. Should you need both, JS can provide you with the perfect solution.JS offers professional CNC machining and laser cutting, providing good quality online laser cutting services, transparent laser cutting prices, and good quality laser cutting parts with a simple ordering process.
If you have any machining needs, we can help. We will tailor a solution for you. Based on our extensive experience and advanced equipment, we guarantee quality and complete satisfaction.
Disclaimer
The content of this website is for reference only. JS services expressly disclaims any representations or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information provided. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, design features, material specifications or processes mentioned should not be considered as any commitment or guarantee by JS for products offered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers on its network or other channels. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for confirming their specific needs and product suitability. If you have any questions or need further information, please contact JS directly.
JS Team
JS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. We have over 20 years of experience with over 5,000 customers, and we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal manufacturing,3D printing,Injection molding,Metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with over 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers, ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it is small volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseJS TechnologyThis means selection efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, visit our website:jsmachining.com


Pingback: Online CNC Service | JS Custom Parts, 5% Off Your First Order! - JUSHENG
Pingback: Reduce Costs By 20%! JS Accurately Identifies The Brass Sheet Metal Grade - JUSHENG