Did you ever find yourself in a dilemma when choosing a soft, flexible material for a new product, with too many options to choose from? Even as the soft, smooth touch of TPE material and the high-performance silicone are typically the contenders, they are anything but interchangeable twins. The wrong material choice can lead to product failure, runaway expenses, and even business failure.
According to JS Precision Manufacturing’s actual experience, this article will guide you through the differences between silicone and TPE, such as material definitions, process distinctions, manufacturing traps, and case studies.At the same time, it provides a communication checklist with JS to assist you in making accurate decisions.
Core Answer Summary
| Comparison Dimension | TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) | Silicone (Silicone Rubber) |
| Material Type | Blend of thermoplastic resin + elastomer | Silicone polymer |
| Temperature Range (General Type) | -40°C~120°C | -60°C~200°C |
| Processing Method | Direct injection molding without vulcanization | Injection molding with vulcanization (heating/room temperature), divided into solid/liquid types |
| Recyclability | Recyclable (waste can be reprocessed) | Non-recyclable (cannot be reprocessed after vulcanization) |
| Biocompatibility | Some medical grades pass FDA certification | Medical grades pass ISO 10993 certification |
| Core Application Scenarios | Consumer electronics, general industrial seals | Medical skin contact, food contact, high-temperature environments |
Is JS’s Material Selection Experience Reliable?
JS Precision Manufacturing has over 15 years of hands-on experience in material selection and injection molding, spanning from medical equipment to auto parts, and consumer electronics.
JS not only is aware of the processing requirements of various injection molding parts, but also excels at custom solutions for flame-retardant and medical-grade applications. We also accept small batch trial production orders through our web-based injection molding services.
From application condition study to material limit inspection, JS always remains true to actual requirements. This comparison chart of TPE and silicone is a result of JS’s scientific application experience, with crucial manufacturing data to provide a reliable material selection guide.
Our instructor is current with real-life applications, ensuring precise material compatibility. For trial small-batch production requirements, we offer fast turnaround through our online injection molding services. Choosing us assures a better consistent material choice and we look forward to hearing from you!
What Is TPE And Silicone?
Learning about the primary aspects of TPE and silicone is the first step in choosing the appropriate material. While both are flexible, their core advantages differ significantly from the application scenarios.
TPE: The Flexible ‘Transformer’
High quality TPE material waste can be recycled and reused.It possesses excellent tear resistance (up to 20 kN/m tear strength) and abrasion resistance and therefore can be applied in products that require repeated flexing or direct skin contact, such as grip covers and headphone cable covers.
Silicone: The Stable ‘Saint Seiya’
Silicone is available in two types: solid silicone rubber (HTV) and liquid silicone rubber (LSR). Both have excellent biocompatibility and are suitable for application in medical devices, food contact applications, and high-temperature products, such as baby pacifiers and engine compartment sealants.
Comparison of Basic Properties of TPE and Silicone
| Property Indicator | TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) | Silicone (Silicone Rubber) |
| Main Component | Blend of thermoplastic resin + elastomer | Silicone polymer |
| Processing Method | Direct injection molding without vulcanization | Injection molding with vulcanization (heating/room temperature), divided into solid/liquid types |
| Hardness Range | Shore A 0 – Shore D 70 | Shore A 20 – Shore A 90 |
| Temperature Range (General Type) | -40°C – 120°C | -60°C – 200°C |
| Recyclability | Recyclable (waste can be reprocessed) | Non-recyclable (cannot be reprocessed after vulcanization) |
| Biocompatibility | Some medical grades pass FDA certification | Medical grades pass ISO 10993 certification |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate (not resistant to strong solvents) | Excellent (resistant to most acids, alkalis, solvents) |

Process Battle: Key Differences In Injection Molding
The injection molding processes applied to TPE and silicone directly influence cost and production efficiency. Doing it incorrectly can easily lead to low yield and cost overrun, as well as influencing final quality and market competitiveness of injection molding parts.
Something to note: Improper secondary vulcanization of silicone will result in a shortage of hardness as well as deformation. TPE is effective for large-scale production at a high speed, while silicone, according to the vulcanization process, is less efficient.
Comparison of TPE and Silicone Injection Molding Processes:
| Process Link | TPE | Silicone (Taking LSR as Example) | Difference Analysis |
| Injection Temperature | 160°C – 240°C | 180°C – 220°C | TPE has a wider temperature range and is easier to control |
| Post-vulcanization Requirement | No vulcanization required | Vulcanization required (120°C-180°C, 5-30 minutes) | Silicone requires additional process and time cost |
| Single Product Cycle | 30 seconds – 2 minutes | 5 minutes – 10 minutes | TPE efficiency is 2-5 times that of silicone |
| Mold Material | P20/718H steel | H13 hot work die steel | Silicone requires higher mold material standards |
| Mold Cost (Small-Medium Size) | 5,000 – 15,000 USD | 10,000 – 30,000 USD | Silicone mold cost is 2-3 times that of TPE |
| Mold Production Cycle | 2 – 4 weeks | 4 – 6 weeks | Silicone mold has a longer production cycle |
JS familiar Our TPE and silicone processes offer a high level of yield injection molded parts. Choose us to be more productive. Here is a consultation, and let the productive manufacturing start!
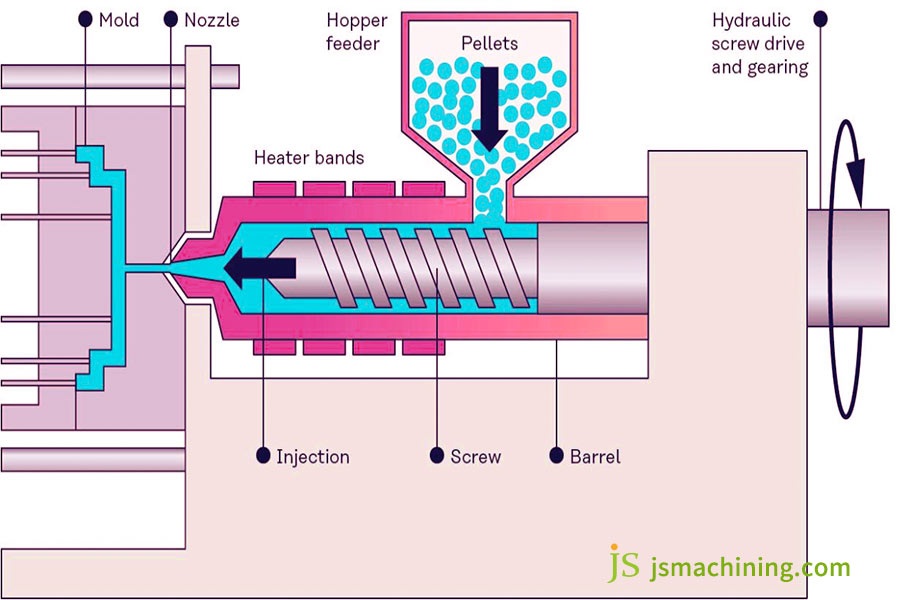
Manufacturing Tips: A Guide To Avoid Product Design And Production Mistakes
In production, avoid material compatibility, dimensional stability, and conformity issues to prevent scrap and additional costs.
Material and Mold Compatibility: Avoid Mold Sticking and Overflow
TPE is prone to mold sticking and requires mold surface treatment (such as nitriding or non-stick coating) and controlled injection pressure of 50-80 MPa. For transparent TPE, supply mold finish (Ra < 0.02 μm). Silicone (especially LSR) is highly fluid and requires mold sealing (mold clearance < 0.01 mm). If necessary, supply sealing strips to prevent overflow.
Control of Dimensional Stability: Provide Shrinkage Allowance
TPE shrinkage is 1.5%-3% (lower hardness, higher shrinkage). Allow for this at design stage and adjust the mold on trial production. Silicone shrinkage is lower (LSR 0.5%-1%, HTV 1%-1.5%), but can shrink 0.1%-0.3% upon secondary vulcanization, requiring measurements after vulcanization.
Compliance and Batch Consistency: Avoiding Certification and Quality Risks
Medical/food-contact uses require materials to be compliant: TPE needs to be FDA/EU 10/2011 (medical-grade approved to ISO 10993) approved, and silicone needs to be approved to ISO 10993/FDA 21 CFR Part 177.
Batch consistency should be tested as well: For TPE, check hardness variation, and for silicone, check the level of cure (which should be > 95%). If you require a small pilot run, use online injection molding services for the quick procurement of samples to ensure compliance, minimizing mass production risk.
JS can reduce your scrap. If you desire a small pilot run or big production, we make the verification process fast with online injection molding services. Choose us for less hassle manufacturing processes. We are looking forward to hearing from you!

Decision Crossroads: 5 Key Things To Help You Select The Final Solution
Applicationasse
Silicone for medical skin-mounting applications, food contact applications, or temperature applications (>150°C).TPE material for general temperature applications, consumer electronics, and general industrial seals.
Core Performance
TPE for flexibility and anti-fatigue, silicone for chemical and high-temperature resistance. Choose TPE for limited budgets or trial production of small quantities, silicone for adequate budgets or large-scale, stable, long-term production. Contact JS for price comparison by injection molding.
Process Efficiency
TPE for short-time mass production or frequent design changes, silicone for stable mass production in the long term and high yield.
Compliance Certification
TPE for general industrial RoHS products, silicone for medical use by ISO 10993/FDA food-grade.
Dazed from deciding between TPE and silicone? JS Precision Manufacturing guides you to exclude options based on application, budget, and other factors, and also provides a full injection molding price analysis. Call us now!

Wearable Medical Patch vs. Engine Underbody Wiring Protector: A Material Rivalry In High-End Applications
Case A: Medical-Grade Wearable Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM) Patch
Demand Background
This 0.5mm thick, less than 5g wearable medical device worn on the skin for 14 days requires core demands to be: highest biocompatibility (hypoallergenic), excellent breathability (for skin well-being), soft comfort with a Shore A of 20-30, and chemical resistance to sweat, 75% alcohol wipes, and everyday showering.
JS’s Material Choice and Reasoning:medical grade liquid silicone (LSR)
- Biocompatibility: Medical-grade LSR passed the complete sequence of ISO 10993-1 to 10993-10 tests with an allergy rate of < 0.01%. Medical-grade TPE, however, showed an allergy rate of 0.5% after 14 days of use, below standard.
- Breathability will keep skin healthy: LSR has a breathability of 500g/(m²/24h) but TPE only 100-200g/(m²/24h), easily resulting in skin problems.
- Excellent stability in complex conditions: LSR resists alcohol wipes and sweat with over 90% retention rate for performance after 14 days. TPE easily swells upon alcohol wipes.
Achievements
The ultra-thin (0.3mm) LSR case is a high-end model with the complaint rate by users at less than 0.1% (compared with the industry average of 1.5%). JS has passed FDA 510(k) certification, and its precise processing has pushed its passing rate to 99.2%.
Case B: High-voltage wiring harness protective cover in the engine compartment of a new energy vehicle
Demand Background
The product should be resistant to 300V-800V high-voltage wiring harnesses from high temperature, engine oil, and electrolyte corrosion. The product’s length is 500mm, inner diameter is 20mm, and wall thickness is 2mm.
Core requirements: resistance to long-term temperature of 125°C-135°C, UL94 V-0 flame retardant, vibration resistance of 1000 hours under 10-500Hz vibration, and lightweight design (to satisfy new energy vehicle weight reduction).
JS’s Material Selection and Reasoning:special high-performance TPV (a type of TPE)
- Chemical and oil resistance for engine compartment exposure: Specialty TPV can withstand 500 hours of immersion in engine oil with a less than 5% volume change, while silicone can withstand 15% volume change and crack.
- Balancing Process and Cost: TPV cycle time is 45 seconds/piece, mold cost $8,000,silicone cycle time is 8 minutes/piece, mold cost $20,000. For a mass production of 50,000 units, TPV costs are 57% lower, with a 6-week delivery (silicone will take 10 weeks).
- Lightweighting improves vehicle range: TPV density is 0.95g/cm³, 13.6% lighter than silicone (1.1g/cm³). Using 20 units can reduce vehicle weight by 100g, corresponding to a 0.2-0.3km increase in range.
Achievements
Custom TPV protective cover achieved 100,000km test with a rate of >90% performance retention, surpassing UL94 V-0 and ISO 1879 standards. It is used in various production vehicles. JS uses custom injection molding manufacturing to provide bespoke matte black surfaces and texture to meet automotive interior and exterior requirements.
Are you looking at effective instances in the medical and automotive sectors? JS specializes in custom injection molding manufacturing, replicating our experience and providing custom solutions. We focus on quality and efficiency to meet high-end specifications.
Unconventional But Necessary Specialty Types
Medical-Grade Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)
Low extractables (<10μg/g), ISO 10993/USP Class VI rated, best for implantable medical devices (such as pacemaker seals), stable to various types of sterilization without reduction in performance, $12-18/lb in cost.
Flame-Retardant TP
This special TPE material has green flame retardants, and it meets UL94 V-0/V-1 rating (oxygen index > 28%). It has the same hardness as regular TPE and 500% elongation at break (better than fire-retardant silicone). It is not vulcanized and sells at $4-8 per pound and can be applied to electronic enclosures and harness wire protectors.
Food-Grade Silicone
Approved to FDA 21 CFR/EU 10/2011 (migration limit < 5mg/dm²). Provides heat stability at -40°C to 230°C, suitable for high-heat sterilization of tableware and infant products. Long-lasting for 500 boiling water sterilization cycles with consistent performance. Market price $8-12 per pound.
Conductive TP
Carbon black/metal fiber/graphene integrated, with a volume resistivity of 10⁻³-10³Ω・cm, it can be injection molding, its scrap can be recycled, and is 40%-60% lighter than metal. It’s priced at 60%-70% that of conductive silicone at $6-15/lb. Is ideal for sensor electrodes and conductive contacts.
How To Start Your Project: A Guide To Working With JS
Explicitly stating the following information while making contact with JS can avoid repetitive revisions, save time, and promote project advancement.
Describe the usage scenario and operating environment of the product
Inform JS about the application of the product (medical/automotive/electronics, etc.), operating temperature range (-30°C to 100°C, for instance), medium contact (motor oil/alcohol/food, for instance), and service life to allow JS to narrow the range of material selection.
Quote important performance indicators and testing standards
Specify parameters such as hardness (e.g., Shore A 50±5), tensile strength (e.g., ≥5MPa), and flame retardancy rating (e.g., UL94 V-0). The required standards (e.g., ISO 10993/RoHS) should be identified. Firm standards, if applicable, should be indicated.
Provide the production batch and lead time specifications
Notify the production batch (100 for trial production/100,000 for bulk production) and estimated lead time. JS will recommend a suitable process and quote injection molding prices.
Provide Product Design Drawings and Tolerance Requirements
Provide 2D/3D design drawings with critical dimensional tolerances defined (e.g., ±0.01mm) and critical assembly sizes. If drawings cannot be provided, provide physical samples or dimensions listing. JS will make adjustments based on material shrinkage rate.
Provide Budget Range and Customization Requirements
Be honest about the total cost of the project (e.g., <$50,000) or the selling price per unit product (e.g., <$1), and customization requirements (e.g., color, texture, secondary process). JS will propose cost-effective solutions.
FAQs
Q1: How can TPE and silicone products be easily distinguished visually?
Here are a few tips:
- Burning technique (beware): TPE burns black and strongly smells, producing a hard ash, silicone burns white, odourless, and produces a brittle ash.
- Touch test: TPE is sticky at room temperature, while silicone is smoother.
- Stretching test: TPE slowly recovers and becomes whiter, while silicone quickly recovers and does not become whiter as much.
Q2: How to eliminate odor issue of TPE material?
The odor issue of TPE materials is typically caused by precipitation or degradation of low molecular weight additives (e.g., oil). The countermeasures are: applying high-grade hydrogenated-grade SEBS-based TPE (low odor and low migration), using low-temperature injection molding and the appropriate screw shear force in processing, and adequate post-processing ventilation.
Q3: Which one is better in temperature resistance?
From the perspective of temperature resistance, silicone is significantly better. Ordinary silicone can be used stably for a long time within the range of -60 ℃ to 200 ℃, suitable for scenarios such as engine compartment and high-temperature disinfection. However, TPE has a narrow temperature resistance range and is prone to softening and deformation beyond 135 ℃, making it difficult to meet the performance requirements in high-temperature environments.
Summary
The difference between TPE and silicone is the choice between ‘efficient and flexible all-round’ and ‘reliable and stable specialist.’ It is an art of looking for the best compromise between performance, feel, price, and regulations. No one is a winner, but the perfect protagonist that best fits your product story.
No matter what material you choose, JS Precision Manufacturing offers full support from material selection to custom injection molding production, utilizing 15 years of hands-on expertise to help you bring your project to life. Call us today for a free sample kit and personal consultation on your design. Having us work for you will make your product launch easier. We look forward to your trust!
Disclaimer
The content of this website is for reference only. JS series expressly disclaims any representations or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information provided. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, design features, material specifications or processes mentioned should not be considered as any commitment or guarantee by JS for products offered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers on its network or other channels. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for confirming their specific needs and product suitability. If you have any questions or need further information, please contact JS directly.
JS Team
JS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. We have over 20 years of experience with over 5,000 customers, and we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal manufacturing,3D printing,Injection molding,Metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with over 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers, ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it is small volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseJS TechnologyThis means selection efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, visit our website:jsmachining.com


Pingback: How Long Does It Take To Plastic Mold Injection? - JUSHENG